According to the Hepatitis B Foundation, an infant may receive the vaccine in three or four doses: Three-dose vaccine series: Medical professionals recommend that all medically stable
No Link Between MMR Vaccine and Autism, Even in High-Risk Kids – NIH Director’s Blog
What about an accelerated schedule? Generally doctors advise against an accelerated schedule since it requires a 4th dose in order to provide long term protection. It’s hard enough to get people to adhere to the 3-shot schedule. Planning for a 4th dose in a year is a challenge. What happens if you are pregnant; is it safe to get vaccinated?
Source Image: healthline.com
Download Image
Jun 18, 2022Adults Who Should Get It? Side Effects Frequently Asked Questions Hepatitis B (sometimes referred to as hep B) is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). It typically causes symptoms like stomach pain, dark urine, fatigue, fever, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), diarrhea, vomiting, and clay-colored stools.

Source Image: sages.org
Download Image
NICU Series Part 5: Vaccination Considerations in the NICU — tl;dr pharmacy Aug 19, 2022A hepatitis B vaccine is now recommended for adults ages 19 to 59 years without risk factor screening and disclosure. This helps increase vaccination coverage and decrease cases.

Source Image: en.wikipedia.org
Download Image
Is One Dose Of Hep B Vaccine Enough Reddit
Aug 19, 2022A hepatitis B vaccine is now recommended for adults ages 19 to 59 years without risk factor screening and disclosure. This helps increase vaccination coverage and decrease cases. TwoDose Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule for Adults. In November 2017, a vaccine was approved by the FDA for use in the U.S. Heplisav-B (Dynavax) is a two-dose vaccine approved for use in adults aged 18 and older. The vaccine is administered as two doses given one-month apart. Ask your doctor about the 2-dose vaccine.
Hepatitis B vaccine – Wikipedia
The new recommendation adds to the existing one for universal infant HepB vaccination and for anyone <19 years who is unvaccinated for HepB. 1 HepB vaccination remains recommended for How effective is the Hepatitis B vaccine? If my wife is infected and I am vaccinated can I still get it? – Quora
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Understanding hep B nonreactive test results and next steps The new recommendation adds to the existing one for universal infant HepB vaccination and for anyone <19 years who is unvaccinated for HepB. 1 HepB vaccination remains recommended for

Source Image: medicalnewstoday.com
Download Image
No Link Between MMR Vaccine and Autism, Even in High-Risk Kids – NIH Director’s Blog According to the Hepatitis B Foundation, an infant may receive the vaccine in three or four doses: Three-dose vaccine series: Medical professionals recommend that all medically stable
Source Image: directorsblog.nih.gov
Download Image
NICU Series Part 5: Vaccination Considerations in the NICU — tl;dr pharmacy Jun 18, 2022Adults Who Should Get It? Side Effects Frequently Asked Questions Hepatitis B (sometimes referred to as hep B) is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). It typically causes symptoms like stomach pain, dark urine, fatigue, fever, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), diarrhea, vomiting, and clay-colored stools.

Source Image: tldrpharmacy.com
Download Image
Adult immunization against hepatitis B: Does the number of jabs matter? – ScienceDirect One month after the first dose of vaccines, the rates of arbitrary seroprotection, defined as the presence of a hepatitis B surface antibody titer > 10 mIU/mL, in the single-dose and double-dose groups were 87.2% and 93.2%, respectively, and the difference was not significant (P = 0.64).

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
NICU Series Part 5: Vaccination Considerations in the NICU — tl;dr pharmacy Aug 19, 2022A hepatitis B vaccine is now recommended for adults ages 19 to 59 years without risk factor screening and disclosure. This helps increase vaccination coverage and decrease cases.

Source Image: tldrpharmacy.com
Download Image
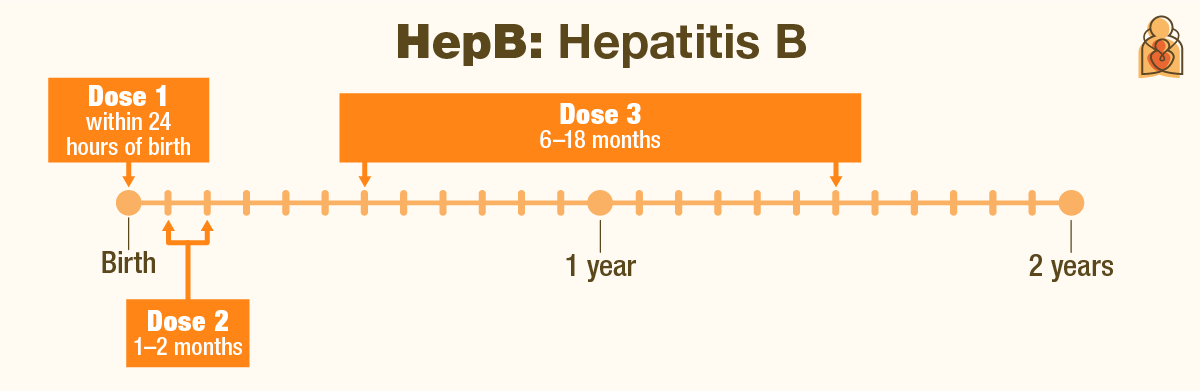
Vaccines Your Child Needs by Age 6 – HealthyChildren.org TwoDose Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule for Adults. In November 2017, a vaccine was approved by the FDA for use in the U.S. Heplisav-B (Dynavax) is a two-dose vaccine approved for use in adults aged 18 and older. The vaccine is administered as two doses given one-month apart. Ask your doctor about the 2-dose vaccine.
Source Image: healthychildren.org
Download Image
Understanding hep B nonreactive test results and next steps
Vaccines Your Child Needs by Age 6 – HealthyChildren.org What about an accelerated schedule? Generally doctors advise against an accelerated schedule since it requires a 4th dose in order to provide long term protection. It’s hard enough to get people to adhere to the 3-shot schedule. Planning for a 4th dose in a year is a challenge. What happens if you are pregnant; is it safe to get vaccinated?
NICU Series Part 5: Vaccination Considerations in the NICU — tl;dr pharmacy NICU Series Part 5: Vaccination Considerations in the NICU — tl;dr pharmacy One month after the first dose of vaccines, the rates of arbitrary seroprotection, defined as the presence of a hepatitis B surface antibody titer > 10 mIU/mL, in the single-dose and double-dose groups were 87.2% and 93.2%, respectively, and the difference was not significant (P = 0.64).